Not long ago, I used PTC Mathcad to uncover some real-world truths about Star Trek and its implausible use of “warp speed.” Of course, Start Trek is fiction, but I thought exploring some of the concepts found in the popular science fiction series would be an interesting way to demonstrate how PTC Mathcad can help you work out physics problems.
Keeping with that theme, this week see how impulse power holds up to the math.
In Star Trek, impulse power is the method of propulsion for sub-light speed travel. It uses the same principles as rocket engines today: Newton’s third law (for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction).
A fusion reaction generates an exhaust, which is directed out of the ship, and the thrust propels the vehicle in the opposite direction.
To bypass some of the trickier real-world physics, the impulse engines of Star Trek also accelerate the exhaust and use driver coils to generate distortions in the space-time continuum just like the warp engines.
Let’s look at the math behind impulse power, and why Starfleet finds it impractical for normal operations.
The Enterprise D has a mass of 4.5 million metric tons, and a maximum sustainable impulse speed of 0.92 c. The impulse engines have a required acceleration of 10 kilometers per second per second, which is just over a thousand g’s.
In Star Trek, it seems like whenever any warp-capable ship travels at less than light speed, it’s almost always “one quarter impulse power.” Let’s use some constant acceleration physics in PTC Mathcad to calculate the time and distance necessary to reach one quarter impulse power:
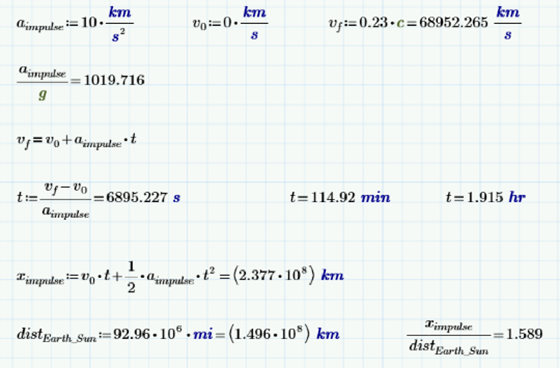
Wow. It would take almost two hours and 1.6 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun!
What about fuel? Let’s calculate how much deuterium (heavy hydrogen) it would take to accelerate the Enterprise to quarter impulse:

That’s the same mass as 337 Empire State Buildings. The Enterprise D only carries 9.3 metric tonnes of deuterium, so they’re a little short.
When people think of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, they mostly associate it with his most famous equation: E=mc2.However, Einstein’s theory revealed two significant ways in which motion affects time and space relative to a stationary observer:
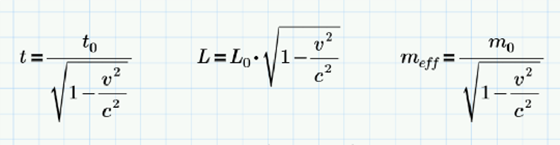
For an object in motion, mass increases, length contracts, and time dilates. This leads to the “Twin Paradox.” In this scenario, one twin stays on Earth, while the other boards a spaceship that travels away from and back to Earth at some fraction of the speed of light. Suppose the traveler’s journey – by her own clock – starts on January 1st and takes one calendar year. When she arrives back on Earth, her twin has experienced a larger passage of time, and is older than her sibling.
Let’s use PTC Mathcad to examine and graph these differences. I create a range variable for fractions of the speed of light, and a function that calculates the time dilation as a function of the speed of light and time traveled. I insert an X-Y Plot, with the range variable along the x-axis depicting fractions of the speed of light, and the function evaluated for the range variable and one year of travel along the y-axis:
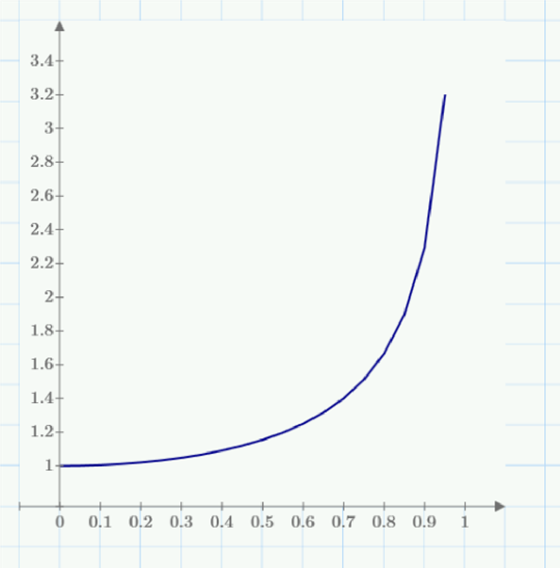
At 0.5 c, the traveling twin’s calendar will say January 1st upon return, but on Earth it’s actually February 25th! At 0.75 c, over an extra half year will have passed. At 0.9 c, and extra 1.3 years would have passed, and at 0.99 c, the Earth-bound sister will now be over six years older than her twin.
Because traveling at impulse speeds for extended periods of time wreaks havoc for subspace communications, computer clocks, and calendar synchronization, Starfleet places a speed limit of 0.25c for routing operations. How much of a difference is that? I’ll write a function that will calculate the difference in synchronization:
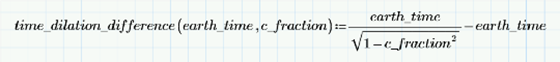
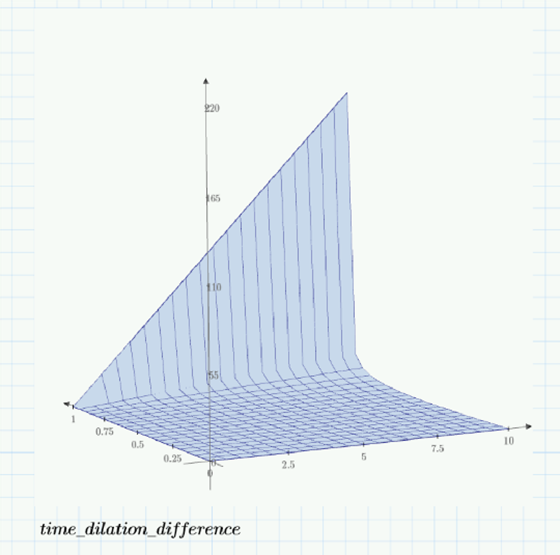
Some 3D plots will help visualize the result. On the left axis, we have fractions of light speed up to 0.9. (At c=1, time dilation and mass increase to infinity.) The right axis shows traveler time. A person taking a 10 year round trip at 0.9c would find more than 200 years had passed on earth.
A “unity plot” verified by calculation shows that traveling at our 0.25c results in our clocks being out of sync by 3.3%:
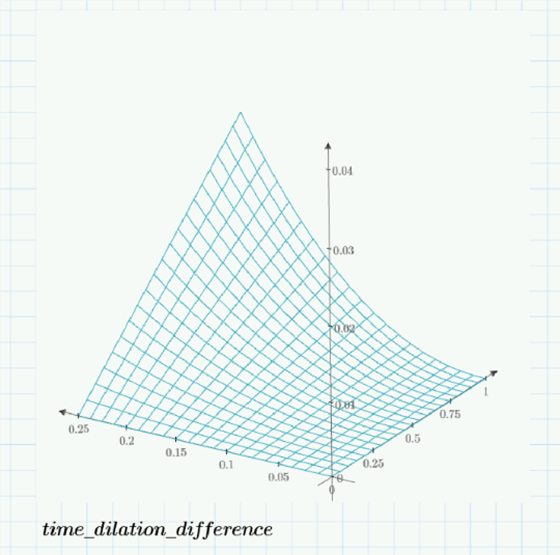
It doesn’t seem like much, but the effects accumulate. We see why traveling for long periods of time at impulse speeds causes such headaches.
“Warp travel” and “impulse power” sound far-fetched – and they are. But it is likely humankind will develop the capability to travel at fractions of light speed someday. Our calculations in PTC Mathcad show that it will take ridiculous amounts of energy and the relativistic effects completely upsets our perceptions of the passage of time. For space travel to be practical, we will need something fantastic from the realms of science fiction, like wormholes, hyperspace, or warp speed.